|

|
|

Buildings galore
 British
& Saxon Royal or Bishop's palaces
covered large areas of land. They were surrounded by an 'enclosure'. Thane's
had smaller enclosures. British
& Saxon Royal or Bishop's palaces
covered large areas of land. They were surrounded by an 'enclosure'. Thane's
had smaller enclosures.- A British enclosure was usually
the walls of a Roman town or the earth ditches and banks of a hillfort.
There would have been a gated palisade (strong wooden wall) on top of
the banks.
- A Saxon enclosure might be made
up of walls (possibly Roman), fences, hedges, earth banks, ditches, rivers or a
combination of these. There would also be entrance gates.
- Within the enclosure were lots
of buildings. The main building would be the great hall (British
or Saxon).
- There might also be a kitchen, a
bower (lord's private room, where the women of his family relaxed and weaved), a toilet block, a pagan
temple or Christian chapel, a meeting
grandstand, a porter's lodge (house for entrance guards), a mill,
granaries (grain storage house) or animal barns.
- Thane's had to own a bell to
call men together in times of trouble. They sometimes had a look-out
tower to keep it in.
- There might also be open or
covered areas for animals, food processing (animal and vegetable) or
industry (woodworking, metalworking,
bone working, pottery, etc).
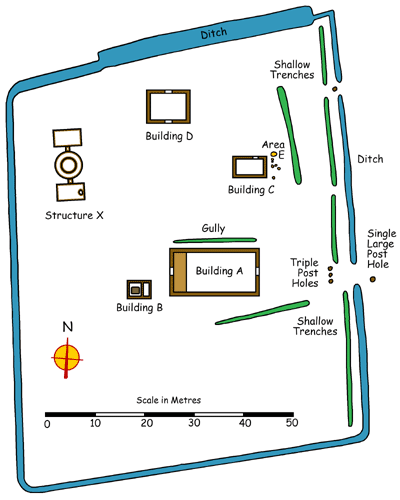
- This is a plan of how the Royal
palace at Cheddar in Somerset looked in the 10th century. The Witan
(king's advisors) met with the king here several times. It was
excavated by archaeologists from 1960 to 1962.
- Can you work out what all the
buildings and other areas were used for? Click
here for some clues.
- Activity
Sheet available.
|

